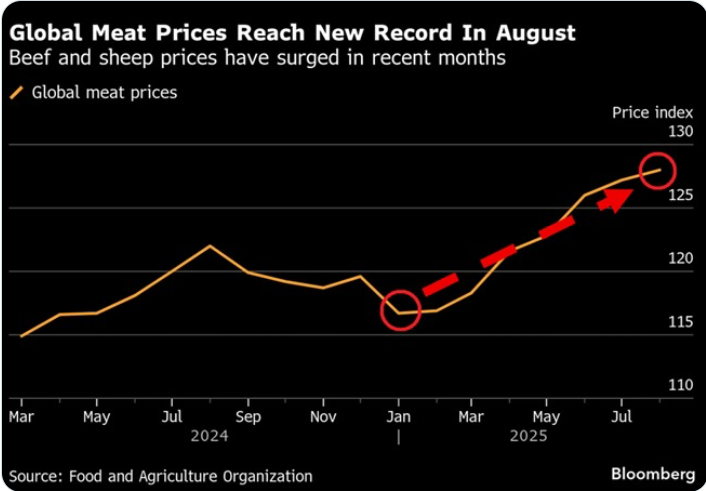
🥩 The global food market is once again under pressure. According to FAO data, in August 2025 meat prices officially reached an all-time high, rising another +10% since the beginning of the year. For millions of consumers, this means steaks, burgers, and cutlets are turning into a luxury, while food inflation shows no sign of easing.
Why is meat getting more expensive?
- USA: The cattle herd has shrunk to its lowest level in decades, limiting supply and pushing prices upward.
- Brazil: One of the world’s top exporters is also reporting herd reductions, affecting global supply chain
- Dairy: Rising milk and dairy prices paradoxically reduce meat supply, as farmers prefer to keep cows for milk rather than slaughter.
- Australia: Strong U.S. demand and tariff restrictions have sharply lifted Australian beef prices.
- China: Increased imports of meat from Brazil, adding further pressure on the market.
- United Kingdom: Beef and veal prices have surged nearly +25% year-on-year.
Impact on consumers
Rising meat costs are putting greater pressure on household budgets, especially in Europe and Asia, where meat traditionally plays a key role in diets. Experts warn that the wave of food inflation could affect not only meat but also related products — from sausages to ready meals.
What’s next?
Analysts predict meat will remain expensive in the coming months. The situation may only change if:
- climate conditions improve,
- herds expand in key producing countries,
- or consumer demand falls due to high prices.
🥦 Meanwhile, more people are considering replacing at least part of their meat consumption with plant-based alternatives. For many families, a “vegan menu” may not be a trendy choice but a forced necessity.
All content provided on this website (https://wildinwest.com/) -including attachments, links, or referenced materials — is for informative and entertainment purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. Third-party materials remain the property of their respective owners.

